Describe the Functions Up to 5 Enzymes Used Fortranslation
Living cells solve this problem by producing proteins called enzymes. Trypsin is another enzyme in the digestive system which breaks protein chains in food into smaller parts.

Expanding The Chemical Substrate Scope Of The Translation Apparatus To Download Scientific Diagram
Help in the formation of macromolecules.

. Transcription is the process by which RNA is replicated from an original template of DNA. They affect every function from breathing to digestion. The general name that chemists use for a chemical entity that increases the speed of a reaction is a catalyst.
Minimize the toxicity of substances. It plays a pivotal role in the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template making it essential to the gene expression that occurs in all known life. It is found in the ribosomes with an enzymatic activity that catalyzes the formation of a covalent peptide bond between the adjacent amino acids.
Lipases for example help digest fat. The reaction takes place as a result. Functions of Enzymes are many like 1.
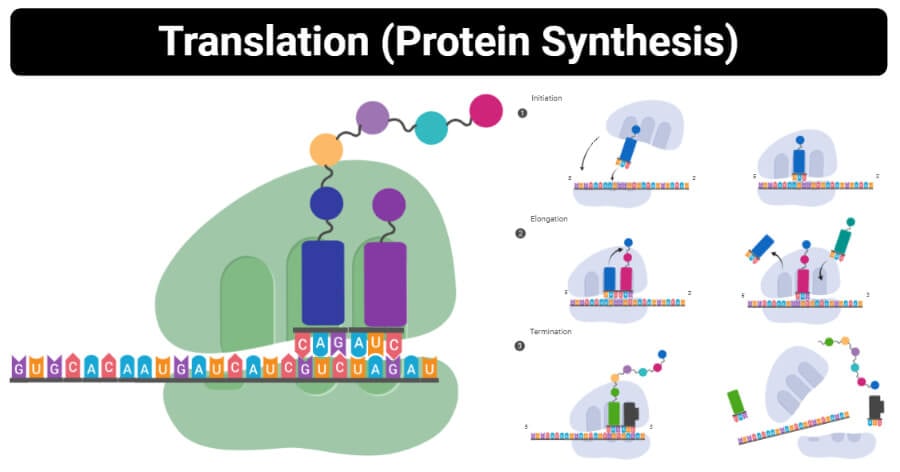
Translation is the process by which the genetic code contained within a messenger RNA mRNA molecule is decoded to produce a specific sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chainIt occurs in the cytoplasm following DNA transcription and like transcription has three stages. Enzymes help speed up chemical reactions in the body. Enzymes are biological catalysts--they catalyze the chemical reactions that happen inside living things.
Other Functions In addition enzymes are also able to generate movement with myosin hydrolyzing ATP to generate muscle contraction and transport intracellular substances around the cell as part of the cytoskeleton. Finally RNA polymerase rewinds the DNA. They are any class of nitrogenous organic compounds which have large molecules composed of one or more long chains of amino acids.
Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase an enzyme catalyzes the bonding between specific tRNAs and the amino acids. Common enzymes involved in these movement mentioned above are myosin ATPase kinesin ATPase and dynein ATPase. They create the conditions needed for biochemical reactions to happen fast.
Enzymes are _____ protein catalysts that _____ the rate of a _____ metabolic reaction without being consumed by the reaction. Enzymes are usually protein molecules that have a dent. Proteins are made from a sequence of amino acids rather than nucleotides.
Control of blood pressure 5. Examples of enzymes and their functions. Takes place in the nucleus during interphase.
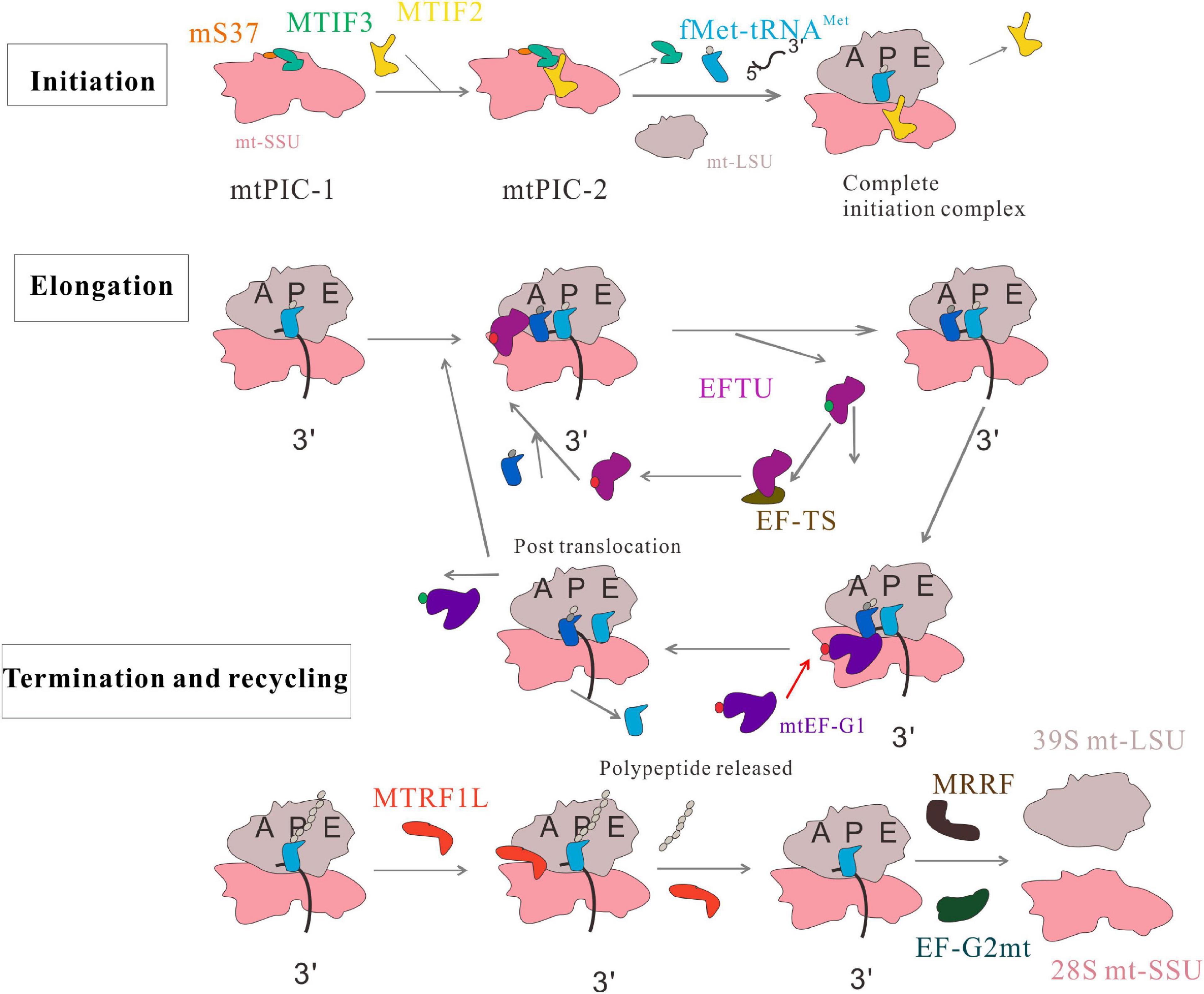
There are two enzymes and four factors involved in translation proccess Enzymes involved- - fMet-tRNA-synthetase only for prokaryotes - attaches N-Formylmethionine to tRNA - Aminoacyl-tRNA-synthetase - attaches amino acid to tRNA - Peptidyl transferase There are a number of non-enzymes that are also used including- - Elongation factors EF-Tu -carries. Betaine helps to maintain a fluid balance inside the mouth. Transferases participate in a myriad of cell reactions.
Aid in the breakdown of large molecules to smaller ones. Examining these five categories of enzymes in detail will make the many important roles of enzymes in the human body more clear. Part 1 Day 1 2.
Transferases are a class of enzymes that transfer specific functional groups from one molecule donor to another acceptor. The main digestive enzyme in the stomach is pepsin which works best at a pH of about 15. Occasionally enzymes are used for medical purposes intended for the treatment of areas of local inflammation.
Enzymes speed up cellular reactions at body temperature by providing a more favourable environment for. These enzymes would not work optimally at other pHs. In order for the conversion of DNA to RNA to occur RNA polymerase must step in and.
Protein Synthesis enzymes and functions. Another function of the enzymes is that they control the amount of energy released by the. Procedure Part 11.
In this article we will discuss the. The enzymes secreted by the mouth mainly provide protection against bacteria. The salivary gland secretes the enzyme lysozyme which has an antibacterial action.
Here are some examples of types of enzymes with some of their functions biological or industrial. Initiation elongation and termination. The objective of this activity is to introduce the concept of enzymes and their functions through the lock-and-key model by using real locks and keys as an analogy.
Proteins are made of amino acids of which 20. Main enzyme in the stomach which chemically digests protein. A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy without being used up in the reaction.
Transferases are implicated in hundreds of different biochemical pathways and are essential to some of most important processes in lives. Enzymes in the human body serve a variety of different functions. Help in the conversion of a molecule from one form to another form.
Peptidyl transferase is the main enzyme used in Translation. In eukaryotes two types of enzymes are used in translation. Enzymes and Their Functions Lock-and-Key Activity Objective.
The oral cavity or the mouth contains salivary glands. Digestion of food 2 metabolism. Help in respiration 7.
Students can be divided in groups of 2 or 3. Enzymes are lifes great facilitators. Transcription and translation are the two processes that convert a sequence of nucleotides from DNA into a sequence of amino acids to build the desired protein.
Enzymes do so by lowering the activation energy needed to start the reaction. What Role do Enzymes Play in Metabolism. Ran polymerase unwinds the DNA.
Control nervous system 6. Up to 24 cash back Enzymes are part of the group of chemicals called proteins. RNA polymerase help make the necessary covalent bonds forming a single strand of RNA that is complementary to the DNA strand.
Breaks the peptide bonds adjacent to arginine or lysine. These two processes are essential for life. They are found in all organisms eukaryotic and prokaryotic.
The enzyme peptidyl transferase connect A site and P site by forming a peptide bond the nitrogen carbon bond during elongation phase. Convert lipophilic molecules to hydrophilic ones. For example different categories of enzymes include digestive enzymes metabolic enzymes liver enzymes nucleases and receptor enzymes.
In this dent the materials to react fit and the enzymes starts pressing on them. RNA nucleotide joins up by complementary base pairing rule u with a g with c. RNA poylmerase is the enzyme involved in transcription.
Trypsin works in the small intestine which is not an acidic environment. Proteins along with carbohydrates and fats are the chemicals that make up most of the diet of animals. The place on an enzyme where the substrate binds.
Ptyalin- Converts starch to simple soluble sugars.
Frontiers Mitochondrial Protein Translation Emerging Roles And Clinical Significance In Disease Cell And Developmental Biology
Protein Synthesis Translation Definition Enzymes Steps Inhibitors

Models For Translation Initiation Regulation See Text For Details Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment